Principles
For professionals, an expert search is available by means of an option to be activated below the search field of a search list.
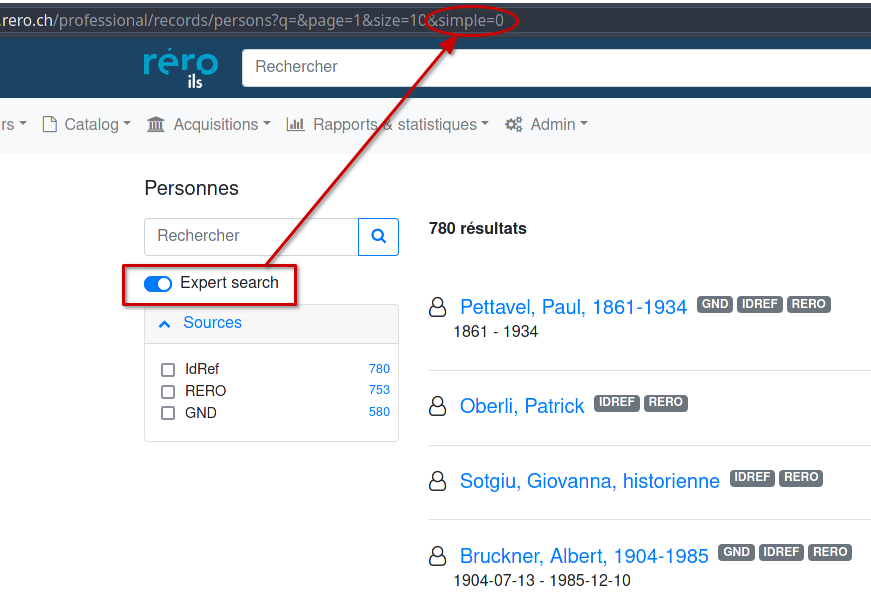
Once activated, the URL parameter changes to simple=0 and the search field allows you to enter more complex and precise queries. This search mode works in exactly the same way as the API, which allows you to see the raw data of RERO ILS resources in JSON, without the interface's display formatting.
It is also possible to carry out an expert search in the public interface, but the parameter must be manually modified by adding &simple=0 in the search URL, and this parameter is reinitialized if the query is modified from the search field.
When activating the option (simple=0), the search input field accepts more complex and precise queries. However, this search mode has the following consequences:
Building searches
To build an expert search, two tools are available and can be combined:
- URL parameters are predefined by the system to facilitate frequent queries. These parameters also control the display of search results and the filtering facets. In the URL, the parameters are separated by a
&symbol. - Elasticsearch query string queries target one or more fields in the index, and are entered after the
q=parameter.
URL parameters
Parameters are the elements in the URL after the question mark. They are combined with each other using the & symbol.
| Parameter | Use | API example | Interface examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource PID | Accesses a specific resource The user interfaces return the detailed view of the resource, and the API returns the raw record as stored in the database without the indexing enrichments. ( See: Fields mapping) |
api/items/1000 |
pro |
q |
Introduce an Elasticsearch query | api/documents/?q=mountain |
public / pro |
page |
Set the number of the displayed results page | api/documents?q=mountain&page=5 |
public / pro |
size |
Set the number of elements displayed in each results page | api/documents?q=mountain&size=25 |
public / pro |
sort |
Define how the results are sorted. The possible sort options vary according to resources. | api/documents?q=mountain&sort=title |
public / pro |
simple |
Define whether simple or expert search syntax applies. This parameter is only relevant for the interface and not for the API, where only expert search is accepted. |
api/documents?q=mountain&simple=0 |
public / pro |
prettyprint |
Format the JSON display | api/documents/?q=mountain&prettyprint=1 |
disponible seulement via l'API |
identifiers |
Document-specific filter allowing combined search by identifier type and value (ISRC in the example, but also applies to ISBN, ISSN and all identifier types) | api/documents/?identifiers=(bf:Isrc)702391010582 |
public / pro |
fulltext |
Document-specific filter to search not only metadata, but also the textual content of attached files | api/documents/?q=sikkim&fulltext=true |
public / pro |
new_acquisition |
Document-specific filter for searching new acquisitions (details and examples under New acquisitions). | api/documents/?new_acquisition=2020-08-01:2020-09-01 |
public / pro |
| Other preset filter | Apply a filter preset by the system. | api/documents?q=mountain&document_type=docmaintype_comic |
public / pro |
Query syntax
A query is entered using the q parameter. The possibilities of the query syntax are described in detail in the Elasticsearch documentation: Query String Syntax.
An expert query allows you to target fields or sub-fields of the resource using the index names of these fields. Each . in a query indicates that a sub-field is being searched, and the : introduces the value sought. This is why it is important to be familiar with the RERO ILS data model when constructing an expert query. For example, provisionActivity.place.country:sz searches for the value sz in country which is a subfield of place, itself a subfield of provisionActivity in the document index.
In some cases, the backslash is used in queries, to allow certain characters to escape processing by Elasticsearch. In a browser's address bar, this backslash must be encoded in URL format: %5C. For example, the * operator, which searches in all subfields of a structured field, must be escaped: %5c*.
Operators
| Opérator | Description | API example | Interface Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
Search in multiple subfields (\*) |
Includes all subfields of entity, so also name variants and parallel forms |
api/documents/?q=contribution.entity.%5c*:"Righetto, Matteo" |
public / pro |
Boolean AND |
api/documents/?q=contribution.entity.%5c*:(Righetto AND Matteo) |
public / pro | |
Boolean OR |
api/documents/?q=contribution.entity.%5c*:(Righetto OR Matteo) |
public / pro | |
Boolean NOT |
api/documents/?q=contribution.entity.%5c*:(Righetto NOT Matteo) |
public / pro | |
Existence of a field (_exists_:<field name>) |
api/documents/?q=_exists_:bookFormat |
public / pro | |
Phrase " |
api/documents/?q=title.%5c*:"à la recherche du temps" |
public / pro | |
| Regular expression | Patrons with postal codes starting with 19, followed by two other digits | api/patrons/?q=postal_code:/19[0-9]{2}/ |
pro |
?q=subjects.\*:(moutain AND Matterhorn) : documents with "mountain" AND "Matterhorn" in the subject field) or multiple subqueries (?q=subjects.\*:moutain AND contribution.\*:"ramuz" : documents with "mountain" in the subjects field AND "ramuz" in the contribution field).Interface: building an advanced query
In professional view, when "Expert search" mode is activated, a form lets you target specific fields and combine them with Boolean operators.
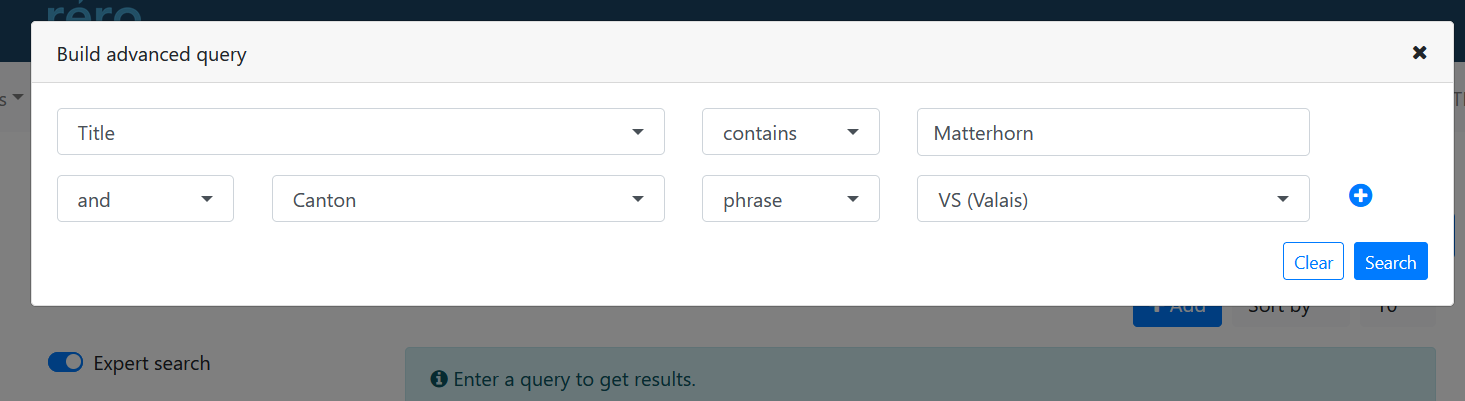
- Contains: Searches for any of the terms entered in the specified field.
- Phrase: Searches for the expression entered in the specified field (all terms in order with field analysis according to index)
By clicking on "Search", the form is translated into the expert search syntax described above and used to search for documents. The query created can then be modified manually or filtered using facets.
New acquisitions
URLs can be built to display the list of new acquisitions, in the public or professional view. Simply add the following filter to the query URL: &new_acquisition=[start date]:[end date]. This filter can be combined with expert searches.
For a detailed list of search examples, see: Search examples